 Internet of Things (IoT) technology and solutions based on it are actively deployed throughout the world. Forecasts say that by 2022, the volume of the Internet of Things market will reach $ 40-50 billion a year. Such growth is caused by several major factors. The main thing is that Internet of Things users are beginning to understand the full benefits of introducing the internet into their production process. Modern sensors can monitor multiple indicators. Thanks to the use of artificial intelligence, Internet of Things solutions have become “smarter” and are capable not only of responding quickly to events but also of predicting them. This brings added profit to companies by optimizing business processes and making people’s lives easier, safer and more productive. Considering the interest of consumers, Internet of Things service providers are even more involved, because this is a market with great potential, and prospects. Taking a niche in it is a long-term strategy.
Internet of Things (IoT) technology and solutions based on it are actively deployed throughout the world. Forecasts say that by 2022, the volume of the Internet of Things market will reach $ 40-50 billion a year. Such growth is caused by several major factors. The main thing is that Internet of Things users are beginning to understand the full benefits of introducing the internet into their production process. Modern sensors can monitor multiple indicators. Thanks to the use of artificial intelligence, Internet of Things solutions have become “smarter” and are capable not only of responding quickly to events but also of predicting them. This brings added profit to companies by optimizing business processes and making people’s lives easier, safer and more productive. Considering the interest of consumers, Internet of Things service providers are even more involved, because this is a market with great potential, and prospects. Taking a niche in it is a long-term strategy. But the Internet of Things infrastructure is not just sensors, servers and software. It is also a means of communication using different protocols. And the correct choice of protocol depends on how the system works.
But the Internet of Things infrastructure is not just sensors, servers and software. It is also a means of communication using different protocols. And the correct choice of protocol depends on how the system works.One of the main technologies for connecting Internet of Things devices is LoRaWAN (Long Range Wide Area Network) technology. Another technology for which a broad spread is predicted is NB-IoT (Narrow Band Internet-of-Things) technology.
LoRaWAN is a method of modulation of the radio signal. This method was invented and patented in 2008 by Cycleo in France, and in 2012 it was bought by the US company Semtech.
 NB-IoT is a standard for cellular communications. It was developed by the 3GPP consortium to communicate with devices with low data rates. The first version of the standard was introduced in 2016. Two versions of this standard were developed: one was issued by Nokia, Ericsson and Intel, and the other by Vodafone and Huawei.
NB-IoT is a standard for cellular communications. It was developed by the 3GPP consortium to communicate with devices with low data rates. The first version of the standard was introduced in 2016. Two versions of this standard were developed: one was issued by Nokia, Ericsson and Intel, and the other by Vodafone and Huawei.We will compare these two technologies to determine the best scope for each.
1. The cost of network deployment
 NB-IoT operates on a licensed frequency band, therefore a license is needed to implement the NB-IoT network. An organization that has not previously provided mobile services will face some difficulties, because building a mobile network in a competitive environment with existing companies requires large financial investments. For existing companies on this market, it is enough to update the base station software to move to NB-IoT.
NB-IoT operates on a licensed frequency band, therefore a license is needed to implement the NB-IoT network. An organization that has not previously provided mobile services will face some difficulties, because building a mobile network in a competitive environment with existing companies requires large financial investments. For existing companies on this market, it is enough to update the base station software to move to NB-IoT.But, on the other hand, because all operators work on different frequency channels, they do not interfere with each other, which guarantees the quality of customer service.
LoRaWAN – operates on an unlicensed frequency band and therefore no permissions are required to deploy a LoRaWAN network.
2. Battery life
In both technologies, considerable attention has been given to the possibility of operating as much time as possible from battery power. If in the first versions of NB-IoT technology devices they had to “wake up” to synchronize with the network, then in the modern version several energy-saving algorithms have been developed and implemented that allow the device to function for several years without replacing the battery:
- Extended Discontinuous Reception (eDRX) mode – when this mode is on, the device periodically stops the receiver between communication sessions to save energy. This mode is used for devices for which the delay in receiving and transmitting data is critical.
- Power Saving Mode (PSM). When it works in this mode, the device stops the receiver and starts it only after a certain amount of time has elapsed, after which it becomes available again on the network.
The LoRaWAN network works asynchronously. Data from the sensor is transmitted through the LoRaWAN network only if they are. If there is no data and nothing to transmit, the sensors are in sleep mode and save energy.
3. Data transfer speed
The 14th launch of the 3GPP NB-IoT technology enables data transfer at speeds of up to 100-140 Kbps.
The LoRaWAN network was initially designed for a lower speed with a minimum of 300 bps and a maximum speed of up to 50 Kbps.
4. Bandwidth
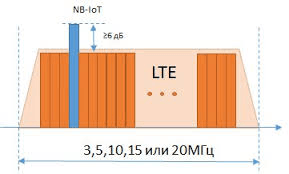 In order to implement the NB-IoT network, a single carrier frequency of 180 kHz is enough. Such a network can be deployed based on an existing LTE transport operator, due to which no additional frequency allocation is required.
In order to implement the NB-IoT network, a single carrier frequency of 180 kHz is enough. Such a network can be deployed based on an existing LTE transport operator, due to which no additional frequency allocation is required.LoRaWAN technology uses from 6 to 9 channels at 125 kHz, i.e. from 750 to 1125 MHz (excluding the distance between the adjacent channels). This is necessary for being able to communicate between the frequency channels in a random order, which makes it possible to reduce the mutual influence, simultaneously with the use of frequencies by several operators.
5. Network coverage
For LoRaWAN, an unlicensed frequency band is used, in the range 864-865, 868.7-869.2 MHz (in the Russian Federation). The State Radio Frequency Board places great restrictions on this area, especially on power levels: no more than 25 MW. In addition, it is forbidden to use the first part of the range at airports. In other places, the transmission cycle of the sensor may not exceed 0.1% of the time. It is easy to calculate that the device can be in transmission mode at most 1.5 minutes a day. Due to this limitation, the system’s capacity is greatly reduced.
At the same time, NB-IoT has a higher signal power margin: approximately + 10 dB, compared to LoRa. Due to this, it is possible to provide reliable coverage in places with difficult radio reception conditions, for example in basements or in metal cabinets with equipment. And if we talk about open areas where the interference is lower than in the urban environment, this advantage allows coverage of the territory with a smaller number of base stations.
6. Cost ratio
If we talk about coverage in open areas, then the number of base stations LoRa and NB-IoT is comparable. If we need a stable operation of the terminal devices inside the rooms and the difficult terrain, using the NB-IoT, thanks to a gain of 10 dB, 3-4 times fewer base stations are needed.
7. The ecosystem
The LoRaWAN network is actively developing it operates in more than 40 countries. The first country that was fully covered by LoRa was the Netherlands. In the world, more than 500 companies are developing devices, writing programs, or providing services to LoRaWAN-based telecom operators.
At this point, LoRaWAN is more widespread than NB-IoT, but NB-IoT uses the best advancements in 4G LTE technology. In addition, it is standardized by the 3GPP international organization and is supported worldwide by network equipment manufacturers (Ericsson, Huawei, ZTE, Nokia, etc.) and final device chipsets (Hisilicon, Qualcomm, Mediatek) and by telecom operators. This will reduce the cost of devices and ensure their mass distribution soon.
Conclusions
LoRa technology can be used both by organizations operating in the mobile communications industry and by those who have no connection with this industry. Moreover, the low cost of the equipment allows the LoRaWAN solution to be used for projects with a limited budget or small projects. On the one hand, this gives independence to the telecom operator, but on the other hand, all issues related to the choice, acquisition, location, maintenance and configuration of data transmission equipment are the responsibility of the organization that has decided to deploy the network.
NB-IoT technology has a higher cost and is therefore only available for deployment for mobile broadband operators. NB-IoT networks are characterized by rare signal transfer delays and high data exchange speeds, which allows it to be used to control processes that are more demanding in terms of speed and reliability than in the LoRa network. We must not forget that the number of wireless devices increases every year, and soon the unlicensed LoRa channel will have many interferences, which is already seen in large cities. At the same time, the NB-IoT uses a licensed frequency band on which foreign equipment cannot function. This minimizes the amount of interference and increases the quality of customer service.
In addition, we must not forget that NB-IoT network operator is concerned with the installation and maintenance of data transmission and storage equipment, which allows the end user to entrust these concerns to professionals.
Based on LoRaWAN and NB-IoT, you can implement a network of any scale. If the main requirements are low price, operator independence and no stringent speed requirements, then we can recommend the LoRaWAN network. If you plan to use the network to control equipment with higher response speed requirements, you need guaranteed packet delivery and you have a budget that allows you to transfer network build and maintenance issues to professionals, then use the NB- IoT would be a more reasonable choice.